Automated Barcode Scanning
Increasing Accuracy in Logistics and Warehousing
Your Guide to Automated Barcode Scanners
Introduction to Automated Barcode Scanning
Automated barcode scanning represents a technological leap forward in inventory management and order fulfillment within the logistics and warehousing sectors. By automating the process of reading barcodes on products and packages, logistics and warehousing companies can significantly enhance accuracy, reduce errors, and streamline their data management.
Types of Automated Barcode Scanners
In the realm of automated barcode scanning, two primary types take center stage. Laser Line Scanners, the more traditional workhorses, are just for scanning one-dimensional (1D) barcodes. On the other hand, Matrix Camera Scanners (Imagers), accommodate both one-dimensional and two-dimensional (2D) barcodes. This section delves into the strengths and applications of each type, providing a nuanced understanding of their capabilities.
The laser line scanner represents the foundational, one-dimensional barcode scanning technology. Although considered somewhat dated in the current tech landscape, it remains a cost-effective and efficient choice for specific applications.
Matrix camera scanners, also known as imagers, represent the cutting edge of barcode scanning technology. They have evolved significantly over the past decade, offering versatile capabilities.
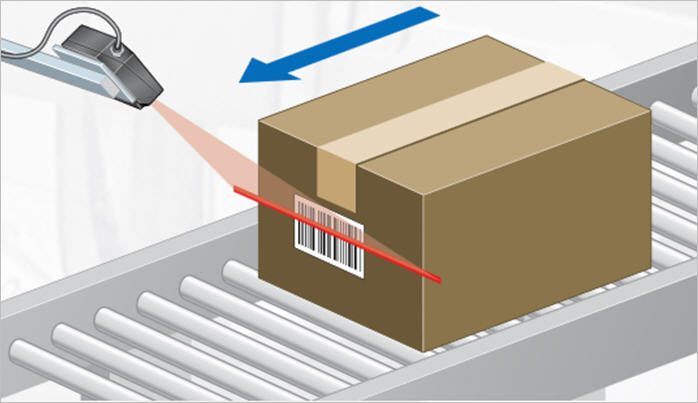
Applications in Warehousing
The applications of automated barcode scanning in warehousing are diverse and transformative. From meticulously tracking inventory movements to optimizing order fulfillment processes, these scanners become integral components of an efficient logistics ecosystem. Explore real-world scenarios where automated barcode scanning plays a pivotal role in ensuring the seamless flow of goods through the warehouse.
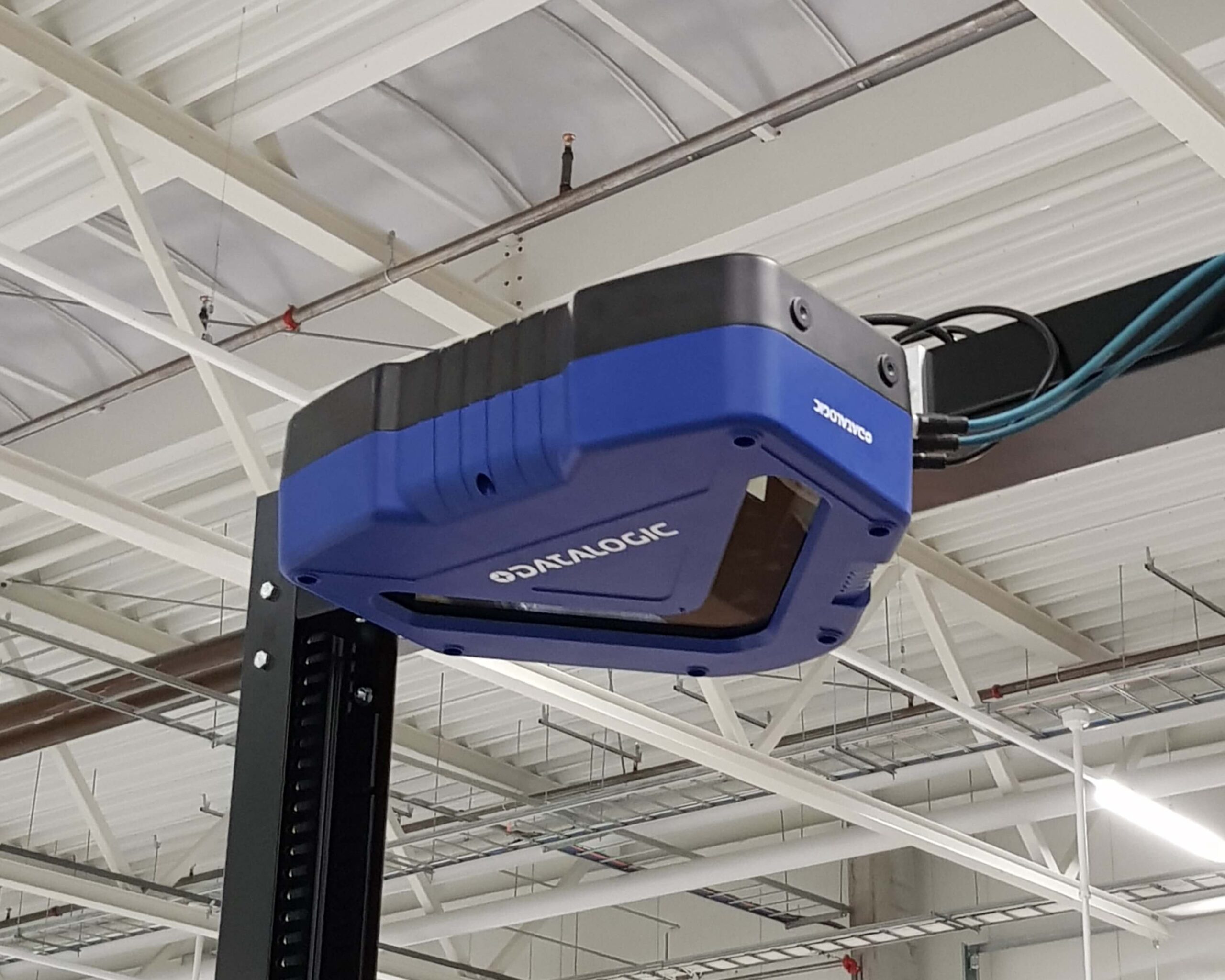

Benefits for Operations
The adoption of automated barcode scanning yields a plethora of benefits for operational excellence. Improved accuracy in data entry, real-time visibility into inventory levels, and increased overall productivity are just a few advantages. Uncover how these systems mitigate the risk of manual errors, reduce processing times, and contribute to the overall efficiency of warehouse operations.
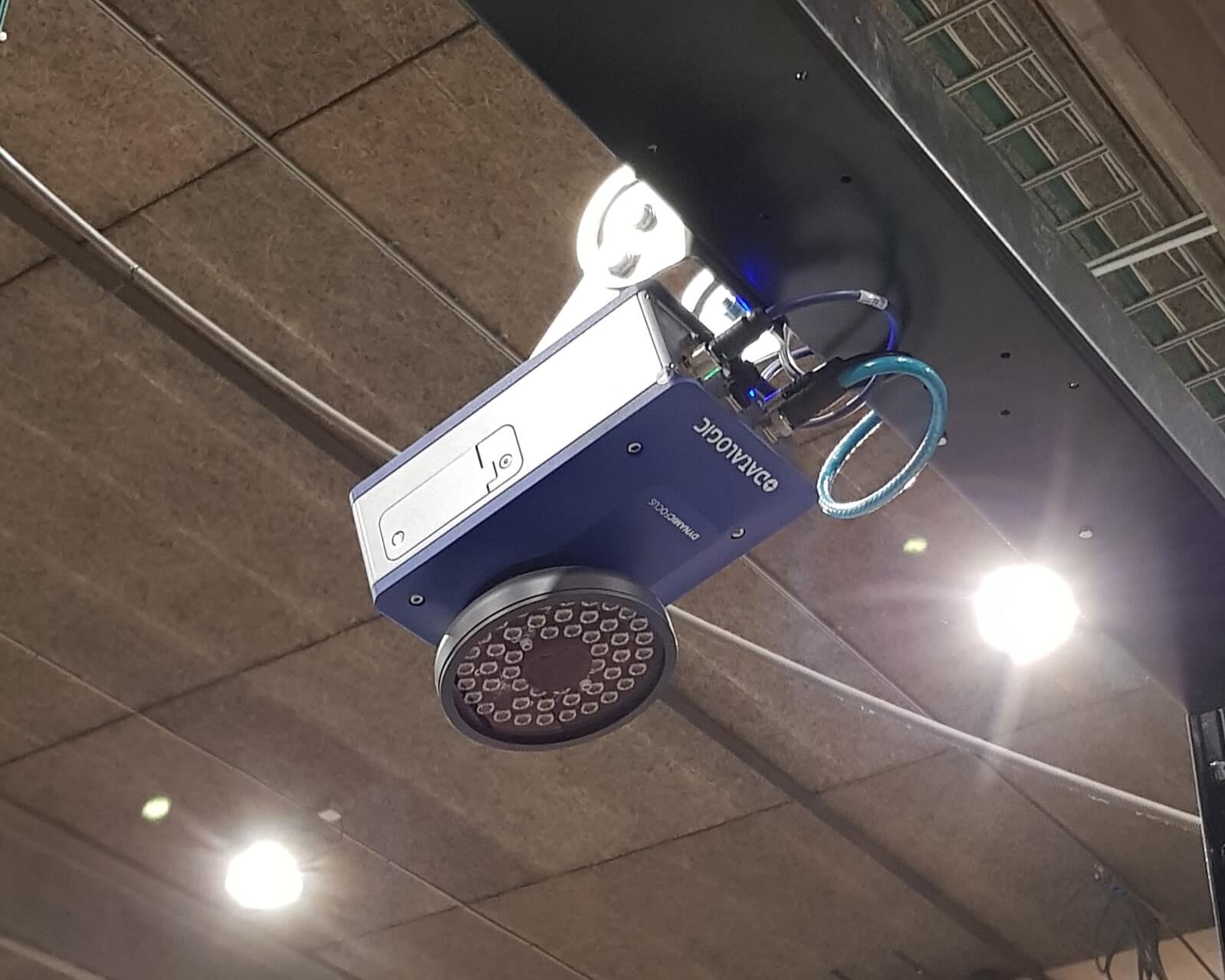

Integration with Technology
The synergy between automated barcode scanning and other technologies is a key aspect of its effectiveness. From handheld scanners used by warehouse personnel to fixed-position devices strategically placed over and around conveyors, these systems seamlessly integrate with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems.
Automated barcode scanning also works well together with dynamic weighing and dimensioning technologies to form data capture systems known as DWS (Dimensioning, Weighing, and Scanning) or Checkweigh Cube systems.

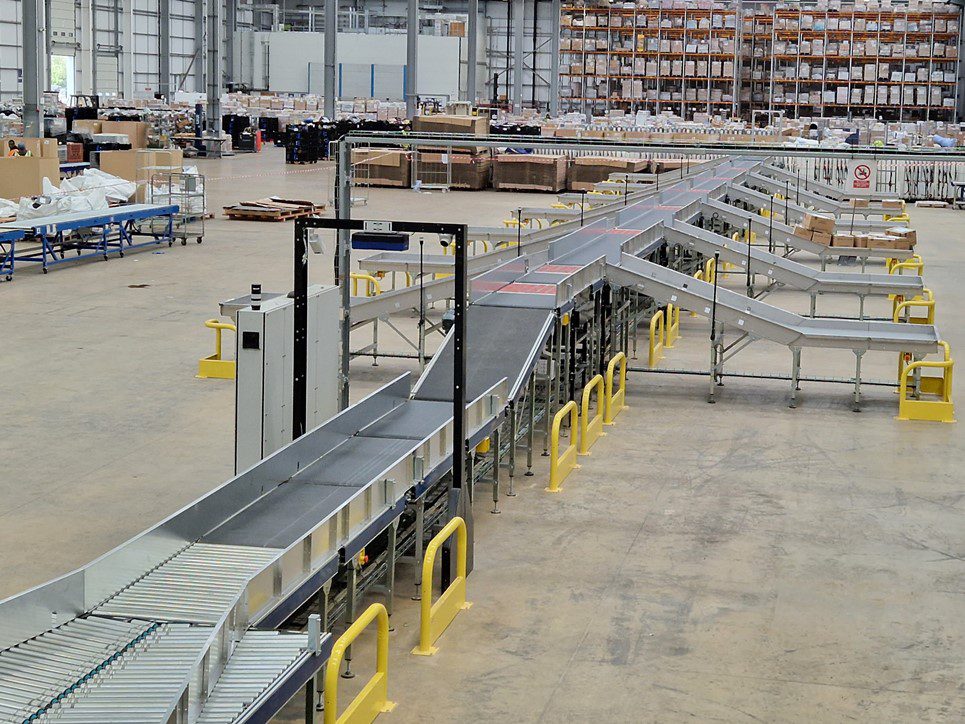
Automated Barcode Scanning & Sortation
Automated barcode scanning plays a pivotal role in enabling real-time decision-making within sortation processes. As parcels move through the sortation system, the instantaneous capture and processing of barcode data provide crucial information for routing and sortation.
This efficiency not only accelerates the sorting process but also allows for dynamic adjustments based on changing conditions or data.

The Benefits for Tracking Information
The integration of automated barcode scanning with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems enhances tracking capabilities throughout the supply chain. Real-time updates on the location and status of each parcel enable logistics professionals to make informed decisions regarding routing, prioritization, and resource allocation. This level of visibility ensures that any disruptions or deviations from the planned route are promptly identified and addressed.
Key Benefits
High Speed Barcode Capture
Scan a wide range of items
Scan all sides of an item
Request a Demo
Close